-
再生医学分野Division of Regenerative Medicine
-
幹細胞分子医学分野Division of Stem Cell and Molecular Medicine
-
幹細胞移植分野Division of Stem Cell Transplantation
-
幹細胞生物学分野Division of Stem Cell Biology
-
再生発生学分野Division of Mammalian Embryology
-
幹細胞加齢医学分野Division of Stem Cell Aging Medicine
-
体性幹細胞研究分野Division of Somatic Stem Cell Research
-
FACSコアラボFACS Core Laboratory
再生医学分野Division of Regenerative Medicine
教授:谷口 英樹Hideki Taniguchi「再生医学(Regenerative Medicine)」は、急速に解明の進みつつある発生生物学や幹細胞生物学の新知見を、臨床医学へ応用することを目指す挑戦的な学問領域です。現在、末期臓器不全症に対して臓器移植が有効な治療法として実施されていますが、年々、増大する移植ニーズと比較してドナー臓器の供給量は絶対的に不足しており、再生医療への期待が世界的に高まっています。当研究室では、ヒト多能性幹細胞(iPS細胞)等からヒト臓器を創出するためのオルガノイド培養技術や移植技術を開発し、臓器移植の代替となる新たな治療法を開発する研究を行っています。また、iPS細胞研究において確立した様々な細胞操作技術を「がん研究(Cancer Biology)」に応用し、がん特異的な微小環境を伴うヒト難治癌組織(癌オルガノイド)を人為的に再構成する手法を確立しています。この技術をもとに、癌の再発や転移を抑制するための創薬開発に繋げる研究を展開しています。 Regenerative medicine is a challenging scientific field that is going to convert the pioneering knowledge of developmental biology and stem cell biology to clinical application. For patients with end-stage organ failure, organ transplantation is the only effective treatment; however, the paucity of transplantable organs hinders the application of this treatment for most patients. Recently, regenerative medicine with transplantable organs has attracted attention. Our laboratory is developing a novel therapeutic strategy to substitute organ transplantation. We have established novel organoid culture technologies to reconstruct human organs from stem cells, including human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and we are going to realize transplantation of human liver primordia (liver buds [LBs]) generated from iPSCs for the treatment of liver diseases. Moreover, we expand the established technologies to cancer research and have reconstructed artificial refractory cancer tissue (cancer organoid) with a tumor microenvironment. Based on this unique cancer organoid, we develop a new drug-screening system for compounds to prevent cancer relapse and metastasis.
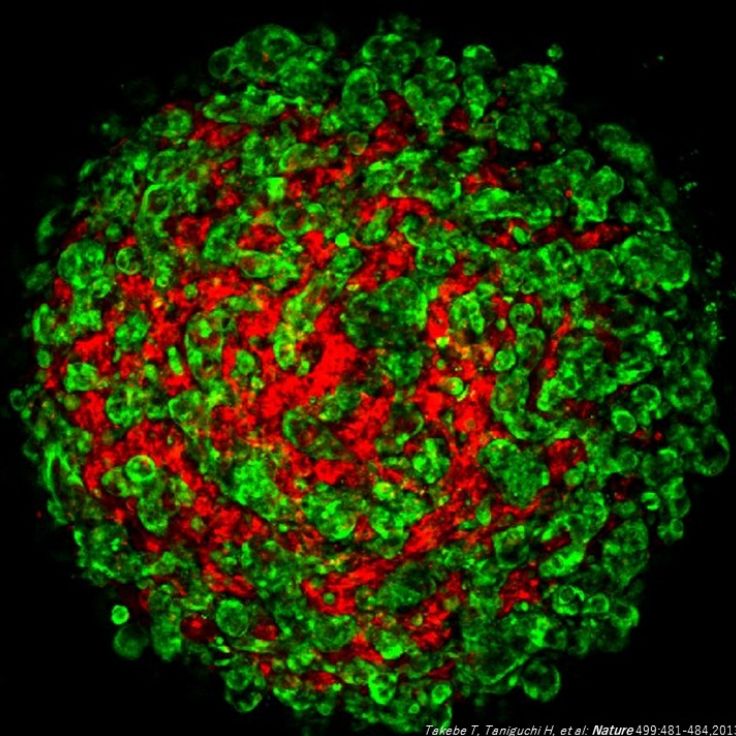
幹細胞分子医学分野Division of Stem Cell and Molecular Medicine
教授:岩間 厚志Atsushi Iwama幹細胞を分子レベルで理解し、応用するUnderstand the nature of stem cells at a molecular level, and apply our knowledge to medicine
幹細胞は自己を複製する能力(自己複製能)および多様な細胞に変化する能力(分化多能性)の両方を有する細胞であり、個体の発生・維持において基幹となる細胞です。当研究室では、幹細胞の自己複製機構の分子基盤を明らかにすることを主題とし、「幹細胞生物学」の真髄となる真理の探究とともに、先端医療の確立に貢献する研究を目指しています。また、幹細胞制御機構の破綻が多くの疾患につながることが明らかになり、その理解も重要なテーマとして取り組んでいます。特に、自己複製能を有する極少数のがん幹細胞の存在が、白血病を始めとして様々な腫瘍で確認されており、がん幹細胞システムと正常幹細胞システムとの異同についても重要なテーマとして研究を進めていきます。これらの研究から得られる知見を、再生医療・がん治療につなげることが最終的な目標です。 Stem cells are a distinct type of cells that are capable of both making a copy of themselves (self-renewal) and changing into a variety of other cell types (multipotency), thus being essential for embryonic development and tissue homeostasis. Our laboratory aims at unraveling the molecular basis for their self-renewal ability, exploring the essence behind stem cell biology, and performing cutting-edge research that contributes to establishment of state-of-the-art therapy. In fact, deregulation of stem cells often results in a wide range of diseases, and we are also working to understand how stem cell deregulation leads to such diseases. In particular, a few self-renewing “cancer stem cells” play a significant role in development and relapse of leukemia and many other types of tumors, and we are interested in what aspect of cancer stem cells is distinct from normal stem cells and therefore therapeutically targetable. Our final goal is to understand molecular mechanisms that regulate stem cell behavior and apply our knowledge to regenerative medicine and cancer therapy.
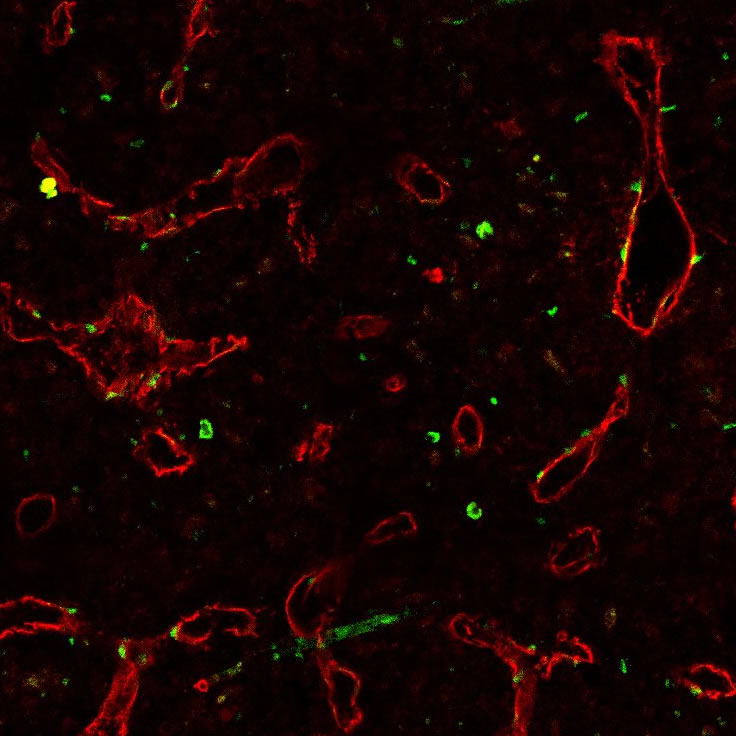
幹細胞移植分野Division of Stem Cell Transplantation
教授:南谷 泰仁Arinobu Tojo当分野はセンターの臨床部門として、医科研附属病院において成人の難治性血液疾患(白血病、骨髄異形成症候群など)の診療を担当し、臍帯血や骨髄を幹細胞ソースとする造血幹細胞移植医療を実践しています。特に臍帯血移植では、世界に先駆けて積極的に推進してきた実績をもとに世界トップクラスの治療成績をあげると同時に、これまで多数の臨床研究を行い、その研究成果を発表しています。また最近では、再発・難治性急性白血病に対するCAR-T細胞療法や移植後の難治性ウイルス感染症に対する特異的T細胞療法など免疫細胞療法の開発にも携わっています。We are conducting clinical stem cell transplantation, especially using cord blood as a promising alternative donor for clinical use and investigating optimal strategies to obtain the best results in this area. Our goal is as allogeneic transplantation to be safer therapeutic option and to extend for older patients.
幹細胞生物学分野Division of Stem Cell Biology
教授:山崎 聡Satoshi Yamazaki私たちは組織幹細胞である造血幹細胞を中心に様々な“幹細胞”に関する基礎研究を通じて、新しい再生医療技術の開発を目指します。Our major goals are to understand the mechanism of the intractable disease and establish the therapy of the disease through the several Stem Cells biology.
造血幹細胞研究を中心とした幹細胞生物学Elucidation of regulatory mechanisms underlying self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells
当研究室では、造血幹細胞をモデルとした幹細胞生物学の研究とその応用に向けた基礎研究を行なっています。近年、様々な多能性幹細胞や成体幹細胞の存在が明らかとなり幹細胞研究分野が大きく発展しつつあります。造血幹細胞は一世紀も前からその存在が考えられ、最も古くから研究と臨床応用に取り入れられた幹細胞です。造血幹細胞研究は幹細胞生物学をリードする分野として走ってきましたが、いまだ不明なことが多くある幹細胞でもあります。これらの疑問に答えるための研究は生物学ならびに医学の分野において非常に重要であり、とても魅力的です。造血幹細胞は個体の一生にわたってすべての血球系を維持することができ、造血幹細胞研究は再生医療、遺伝子治療のさらなる発展に大きく貢献すると期待されます。 Our studies focus mainly on investigation of stem cell biology using the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) as a research model. Recent identification of a variety of stem cell sources including embryonic and somatic stem cells has brought about substantial progress in the field of stem cell research. The HSC represents the first stem cell for which identity and existence were determined. Studies on HSCs have provided us with some basic concepts applying to different types of stem cells, yet many of these concepts remain unverified. It therefore is very important to continue basic studies to answer many questions left unsolved and thus to permit contributions to the field of biological research and clinical medicine. HSCs are capable of continuous supply of all lineages of blood cells to each individual for his or her entire life. We believe that HSC research will eventually make great contributions to the development of safe and efficacious regenerative medicine and gene therapy.
再生発生学分野Division of Mammalian Embryology
特任准教授:小林 俊寛Toshihiro Kobayashi初期胚と多能性幹細胞を駆使し、胚発生を理解し再生医療への応用に繋げるUUnderstanding and application of early mammalian development using pluripotent stem cells and early embryos.
わたしたちの身体はたった一つの受精卵が分裂と運命決定を繰り返すことで作られます。この胚発生がどのように進むか理解することは、受精卵のように未分化な多能性幹細胞から目的の細胞を作り出す再生医療研究において、重要な基盤となります。また胚発生において厳密に制御される臓器形成のしくみをうまく利用することで、動物の体内で多能性幹細胞から目的臓器を作製する研究も進められています。再生発生学分野では、多能性幹細胞、胚発生初期の胚、そしてそれらを人為的に直接操作する発生工学技術を用いることで、初期胚発生機構の理解と、臓器再生などの再生医療への応用を目指した研究を進めています。特に、様々な哺乳動物を用いることで、種を越えた普遍的な分子基盤の解明や、動物種の特徴を活かした技術の開発に力を入れています。 A single zygote can make our body by repeating cell divisions and cell fate decisions. Understanding the process of embryogenesis provides us fundamental information for producing specific cell types from undifferentiated pluripotent stem cells in vitro. Furthermore, the use of organogenesis during embryo development, which is strictly regulated in an elaborated manner, may allow us to generate targeted organs from pluripotent stem cells in vivo. Our lab, division of mammalian embryology, aims to understand mechanisms underlying the cell fate decisions in early mammalian embryos and to apply the principle for future regenerative medicine. In particular, we use pluripotent stem cells and early embryos from various mammals, which will enable us to investigate conserved mechanisms among the mammals and to develop novel technology by the use of species-specific features.
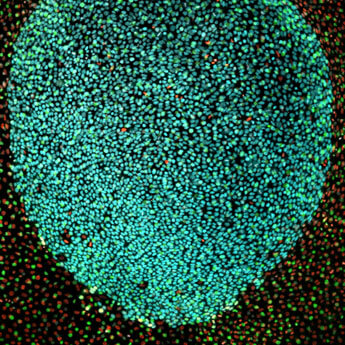
幹細胞加齢医学分野Division of Stem Cell Aging Medicine
教授:西村 栄美Emi Nishimura幹細胞の品質管理と老化の分子基盤を解明し、
その制御による革新的疾患治療と健康長寿を実現Unveiling the molecular basis for stem cell quality control and aging towards innovative treatment of diseases and the extension of health span
幹細胞は、生命の発生から終焉に至るまで生体の恒常性維持と機能の維持において極めて重要な役割を果たしています。わたくしたちは、皮膚の組織幹細胞の同定に始まり、ライフスパンにわたる幹細胞の運命と動態の追跡を通じて幹細胞の自己複製とステムセルエイジングのメカニズムの解明とその制御に取り組んでいます。環境因子や遺伝因子に対応した個々の幹細胞の運命や動態の生体内での解析ならびにオルガノイド技術を用いた解析から、幹細胞の品質管理とその破綻の仕組みが明らかになりつつあります。これらの研究を通じて、幹細胞中心性に進行する組織の再生と老化の仕組み、癌の発生・進展の仕組み、さらに臓器連関や個体老化の仕組みの解明に取り組んでいます。幹細胞の革新的制御技術の開発を通じて老化ならびに疾患の制御、健康長寿の実現へと繋げます。Tissue stem cells play critical roles in tissue homeostasis and function throughout the lifespan of a living organism, from its development to its death. Our research, which started from the identification of tissue stem cells in the skin, is trying to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of stem cell aging by tracking the fate and dynamics of stem cells throughout their life span. Based on the fate and dynamics of individual stem cells in response to environmental and genetic factors in vivo and in vitro with organoid technologies, we are understanding the mechanisms of stem cell quality control and its deterioration. Though those approaches, we are trying to elucidate the mechanisms of stem cell-centered tissue regeneration and aging, cancer development and progression, and inter-organ communication and organismal aging. Through the development of innovative technologies to control stem cells, we aim for the the realization of better treatment and prevention of diseases and extension of health span.
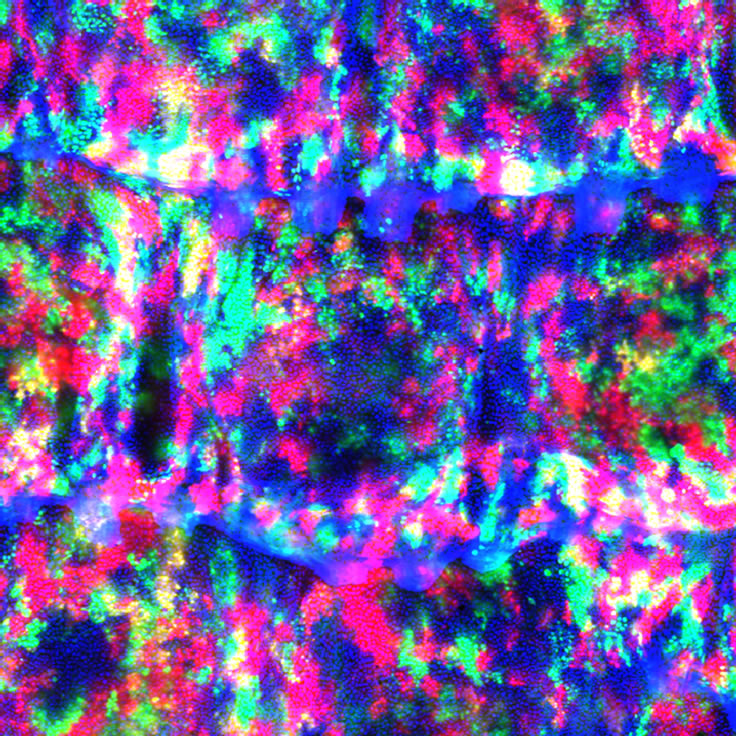
体性幹細胞研究分野Division of Somatic Stem Cell Research
教授:長村 登紀子Tokiko Nagamura-Inoue MD,PhD体性幹細胞(臍帯血や臍帯由来間葉系細胞)の特性を免疫細胞療法や再生医療へ活かすTo apply the somatic stem cells, especially perinatal appendages; cord blood and umbilical cord-derived cells for immuno-cell therapy and regenerative medicine.
体性幹細胞は、間葉系細胞(Mesenchymal Stromal cells;MSC)や血液細胞等の中胚葉系組織に由来する細胞です。特にMSCは、全身臓器の間質に存在し、自己複製能があり、炎症や組織障害部位に遊走し、抗炎症効果や組織修復能を発揮することから、免疫療法や再生医療への応用が始まっています。体性幹細胞研究分野では、そのソースとして臍帯由来MSCに注目し、附属病院臍帯血・臍帯バンクと連携して、その特性を研究し、新たな治療拡大を目指しています。一方で、高品質のMSCソースを得ることは、新規治療法の開発にもつながります。当研究分野では、高品質のMSCソースを提供するために、IMSUT-HLCセルプロセッシング施設を活用し、再生医療等製品やその原料製造を目指しています。Somatic stem cells which are derived from mesoderm, include mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), blood cells, and other mesenchymal tissues. In particular, MSC exists in the interstitium of systemic organs, has self-renewal ability, migrates to inflammation and tissue damage sites, and exerts anti-inflammatory effect and tissue repair ability. Nowadays, it has begun to be applied to immunotherapy and regenerative medicine. In the Division of somatic stem cell research, we have focused on umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) as its source, are studying its characteristics and aiming to develop the new clinical applications in collaboration with the Umbilical Cord Blood and Umbilical Cord Bank of the IMSUT Hospital (IMSUT CORD). In addition, obtaining a high-quality MSCs source also leads to the development of new cell therapy. To serve the high-quality MSCs, we develop to manufacture the UC-MSCs for immunotherapy/regenerative medicine by utilizing the IMSUT-HLC cell processing facility.
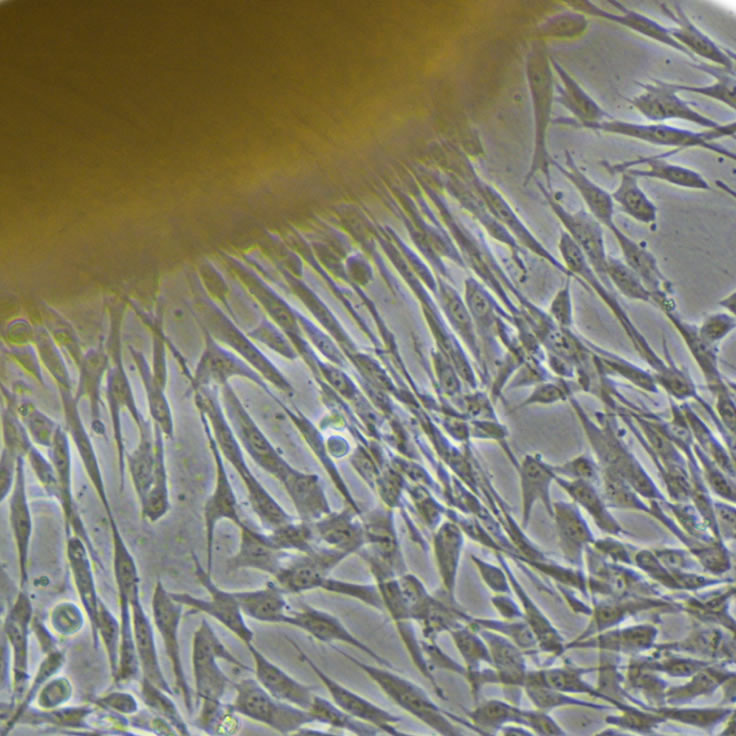
FACSコアラボFACS Core Laboratory
教授:岩間 厚志Atsushi Iwamaユーザーフレンドリーな細胞解析・分離施設 User-friendly center for cell analysis and sorting
フローサイトメーターは細胞を用いた研究には非常に強力なツールですが、研究者にとってその操作の煩雑さから習熟に時間と経験が必要な機器でもあります。FACS コアラボラトリーでは、医科研内外の研究者を対象にフローサイトメトリーによる細胞解析・分離の支援を行っています。FACS使用経験の無い方には、細胞 の処理方法等の相談も受け付けています。幹細胞をはじめとした細胞生物学研究の発展のため、利用者本位の支援を行っています。 Flow cytometer is a very powerful tool for cell research, but also a complex device that requires a fair amount of time and experience before researchers become able to operate it by themselves. The FACS Core laboratory helps researchers analyze and sort cells using flow cytometry, regardless of whether they work at IMSUT or other institutes. For those who do not have experience with FACS, we also offer consultation on how to prepare cell samples. Our aim is to provide user-friendly services with the goal of contributing to progress in cell biology and stem cell research.

